CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
Coronary artery disease is the most common type of heart disease in all over the world. The first sign might be a heart attack. So it’s a major health problem.
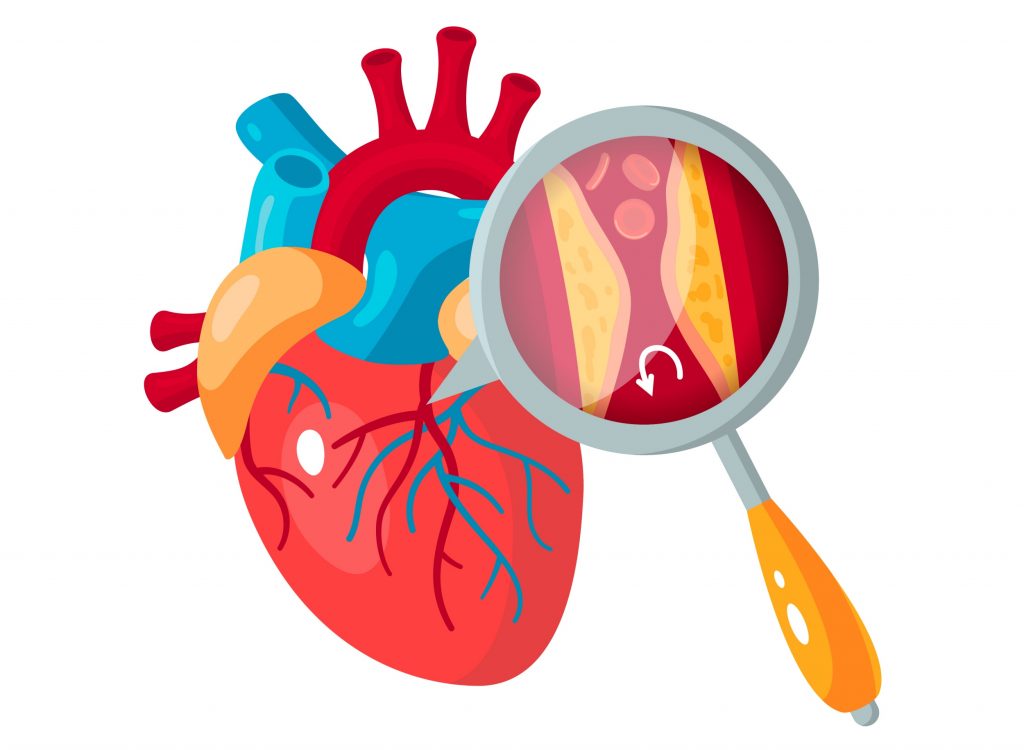
Coronary artery disease is the narrowing or full blockage in one or more arteries called “coronary artery”, which supply blood to the heart muscle. There are two main coronary arteries. Left and Right. The main cause of the disease is the hardening of the vessels, called “atherosclerosis”. Fat accumulations, which occur in the coronary arteries over time, appear in the form of thickening, called “plaque”, which do not cause a complete blockage in the vessel. The subsequent rupture of this plaque and the resulting clot leads to a complete blockage in the vessel.
Symptoms
When the coronary arteries begin to narrow due to plaque formations, the amount of blood supplied to the heart reduces. Especially, in the cases of exercise and excitement when the tissues need more oxygen and energy than usual, the amount of blood sent to the heart does not suffice to supply the heart, leading to fatigue, chest tightness and extremely severe, short-term chest pain called angina, a condition which disappears when the patients take a rest. At this point, the patient must definitely see a doctor. If this blockage in the coronary arteries causes a complete blockage in time, the patient will have a heart attack and the heart muscle will be damaged permanently. A patient who has a heart attack suffers very severe chest pain, which does not go away with rest or it will recur over and over again.
Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease
- Family History
- Smoking
- High Blood Lipids
- Overweight
- Physical Inactivity
Diagnosis
- ECG: Measures the electrical activity, rate and regularity of your heart
- Echocardiogram: Measures the capacity of the heart and checks the status of the valves
- Exercise Test: Helps to determine how well your heart is working when it is pumping more blood
- Coronary artery calcium Scan: Measures the calcium buildup in your coronary arteries
- Coronary Angiogram: Shows the inside of the coronary arteries by injecting a special dye into your arteries
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT OPTIONS?
Treatment options for a person diagnosed with coronary artery disease include medication, opening the blocked vessel by means of balloon or stent method and coronary artery bypass surgery.
Depending on the number of blocked vessels, the severity of the blockage and the localization within the vessel, one of these three treatment methods is preferred.
Medication mainly reduces the severity of the patient’s main complaints such as pain and shortness of breath. Medication also slows down the progression of the disease.
Generally, balloon or stent method is preferred in the case of a blockage in one or two vessels, whereas coronary artery bypass surgery is preferred in widespread blockages involving multiple vessels.
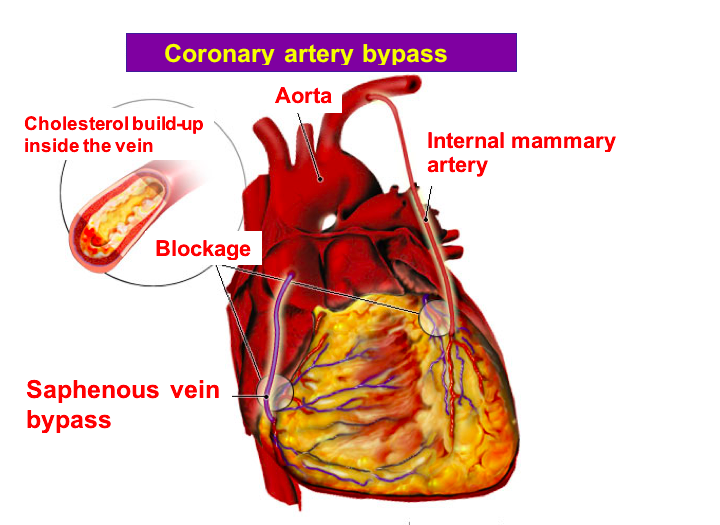
Coronary artery bypass surgery is a bridging operation performed by attaching one end of the artery or vein taken from another part of the body, beyond the obstruction in a blocked vessel. The veins (saphenous vein) used for this purpose are generally taken from the legs and the arteries are taken from underneath the breastbone (internal mammary artery) or from the arm (radial artery).
If the vein taken from the leg or the artery taken from the arm is used, then the other end of the vessel is sutured to the aorta vein, which is the main vessel coming out of the heart. And the blood flow in the artery taken from underneath the breastbone comes directly from the vessel that goes to the arm.
Coronary artery bypass operations are usually performed with the help of a device called heart-lung machine in all over the world. To sew the grafts onto the small tiny coronary arteries we might need to stop the heart temporarily. This device enables the heart and lungs to be stopped during the surgery. Alternatively the operation can be performed without stopping the heart. In this case, we will stabilize the area around the artery to be bypassed with a special instrument. This procedure is also called “Beating Heart Surgery”.
In certain situations a procedure called MIDCAB (Minimally Invasive Direct Coronary Artery Bypass) can be performed. MIDCAB surgery differs from the conventional coronary bypass surgery by not using heart lung machine and not cutting the breastbone. Alternatively coronary arteries can be accessed by a small incision called thoracotomy just underneath the left nipple. The main advantage is cosmetic. However the disadvantages of this technique is it cant be used to treat severely diseased vessels and it can only give access to left side arteries. Basically it is not a technique for every patient.
The patients usually stay in intensive care for 1 days postoperatively.. The length of hospital stay is 5-7 days. It is a period of approximately one month before the patients get back to their daily routine.
