VASCULAR DISEASES
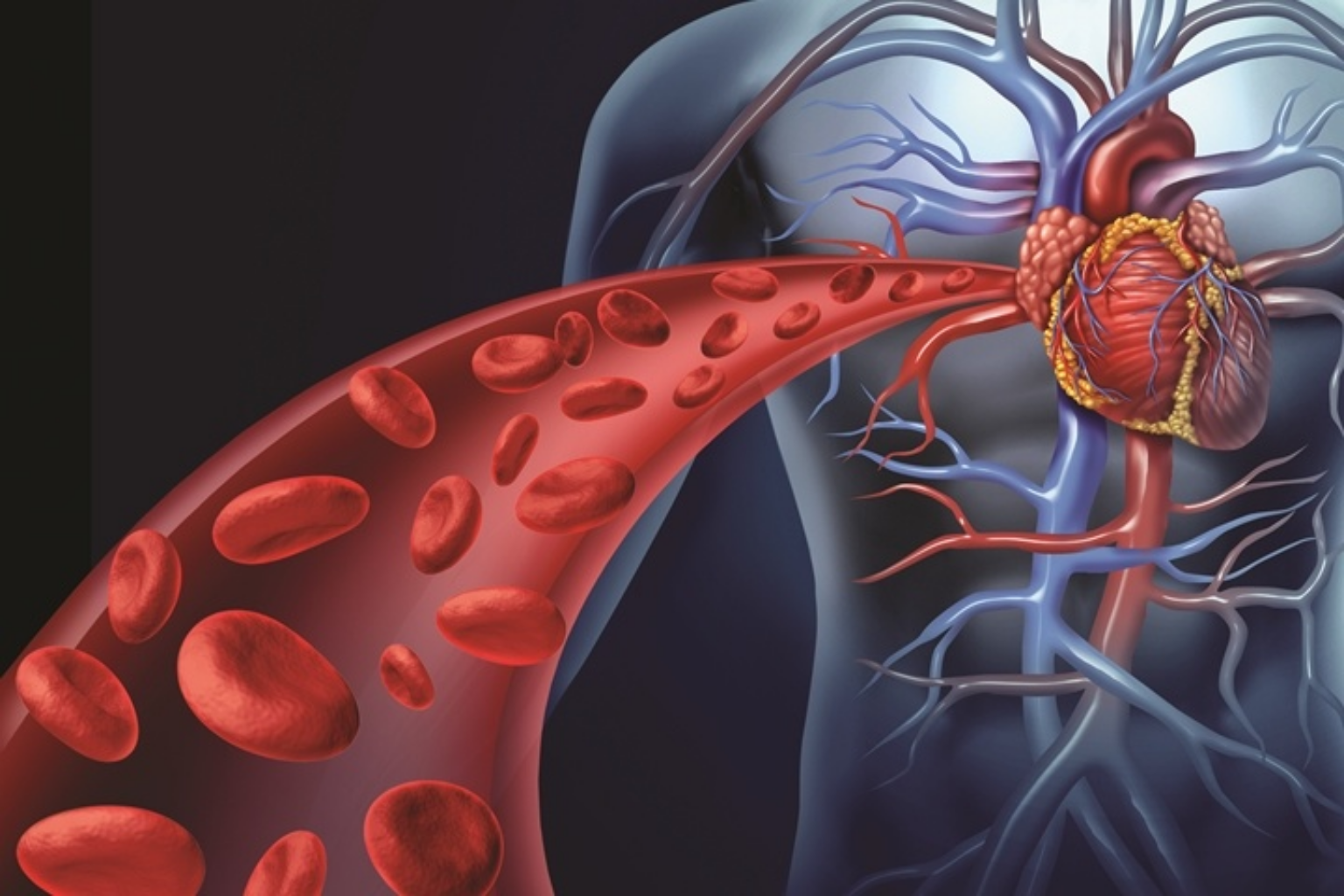
Vascular system is the body’s network of vessels which includes arteries, veins and capillaries. Arteries carry the oxygen rich blood from heart to your tissues. Veins carry the deoxygenated blood back to your heart from the tissues. Capillaries are tiny vessels that connect the arteries and veins. Vascular disease can happen in your arteries or veins.
ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSMS
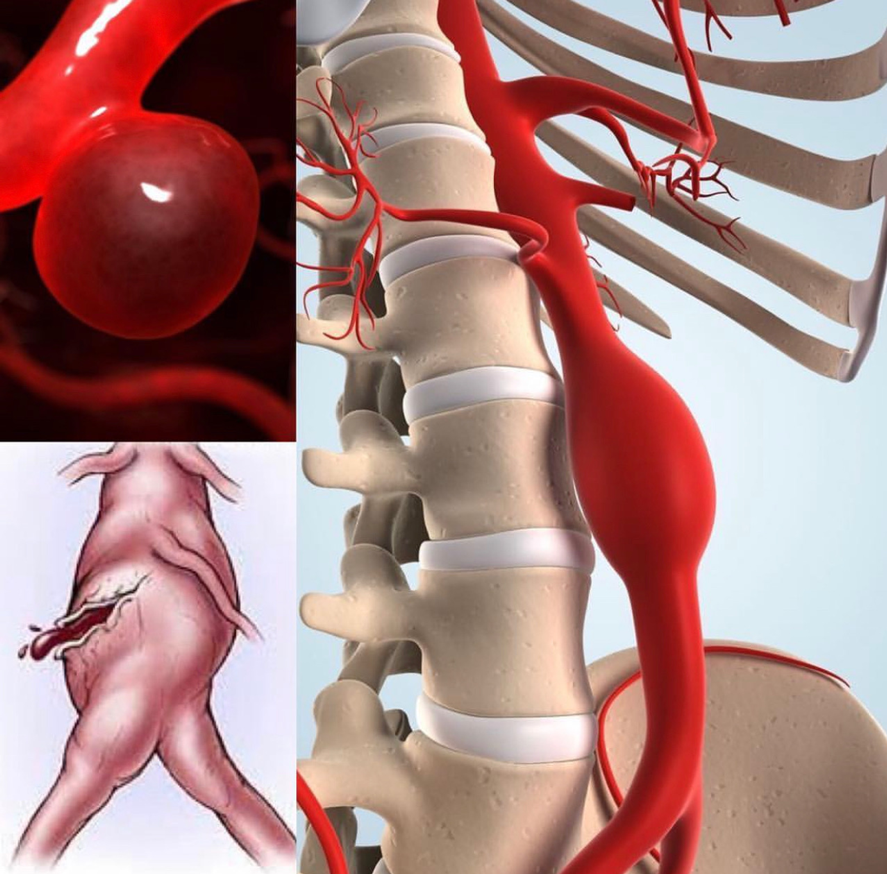
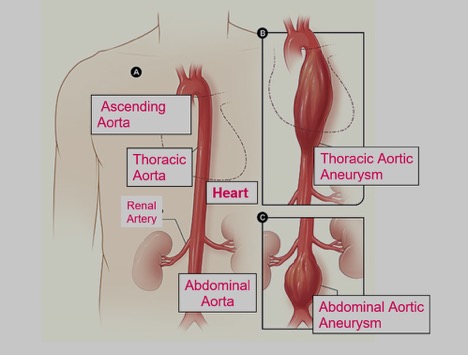
A major sub group among arterial diseases is the widening of the vessel called “aneurysm”. Aortic aneurysms can develop inside the thoracic cavity and / or in the abdominal cavity, starting from the point where the aorta comes out of the heart. Aneurysms of the aorta are called based on its localization. Most aortic aneurysms occur in the abdomimal aorta so called abdominal aortic aneurysm. Aneurysm enlarges and streches the walls of the artery and in some point further stretching is compromised and rupture can occur. This is a fatal complication.
Aneurysms often progress silently. The diagnosis is usually made during an investigation performed for another reason. In these patients, sometimes the first symptom may be rupture of aneurysm.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm is more common in men than in women. It is more prevalent in smoking males above 65 years of age. Patients with a family history of aneurysm and with a known arteriosclerosis are at risk.
How do I notice?
Your doctor may notice your aneurysm during your abdominal examination, but it can often be overlooked. In rare cases, it can be noticed as a pulsating mass in the abdomen. If there is a suspicious condition, it is diagnosed with ultrasonography. Ultrasonography is a painless and simple method.
What are the treatment options?
Surgical treatment will be required depending on the severity of aneurysm. In general, the aneurysms measuring more than 5 cm in diameter should be treated considering the patient’s general condition. It should be noted that the higher the diameter of the aneurysm, the higher the risk of rupture. The rate of survival from a ruptured aneurysm is very low. Your doctor will plan the best schedule for you.
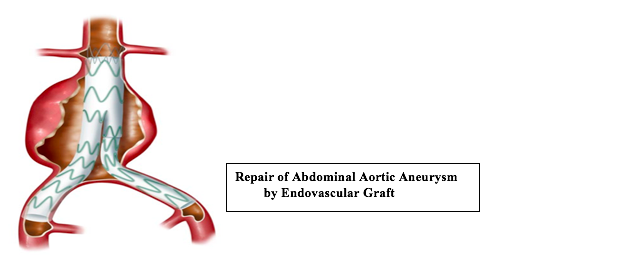
There are two options for the treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms. In the classical surgical intervention called “open abdominal method”, the area with aneurysm is removed and a prosthetic tube graft is placed to the aorta. In the less invasive form which is called endovascular method, involves using a graft to stabilize the weakened walls of the aorta.
What is endovascular repair?
This is a new treatment method that came into existence in the 1990s, as an alternative to the surgical treatment. Unlike the open method, it is a procedure in which stent graft is placed in the area with aneurysm, using the two groin regions, without having to open the patient’s abdomen. Today, 70-80% of the aneurysms can be intervened by endovascular methods. EVAR does not require a large incision and has a substantially shorter recovery time compared to open surgical approach.
CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASE
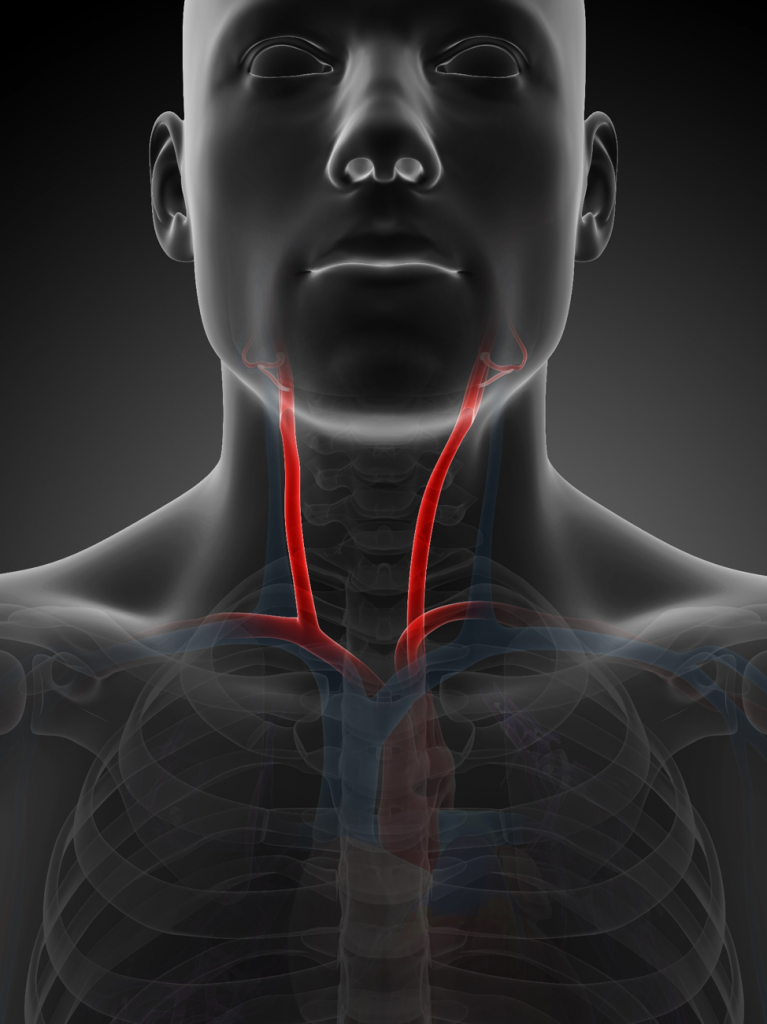
Cerebrovascular disease is a group of conditions that affect the supply of blood to the brain. Restrictions in blood flow may occur from narrowing or blockage of the artery which may end up with an insufficient or lack of flow to the brain tissue and may cause a stroke.
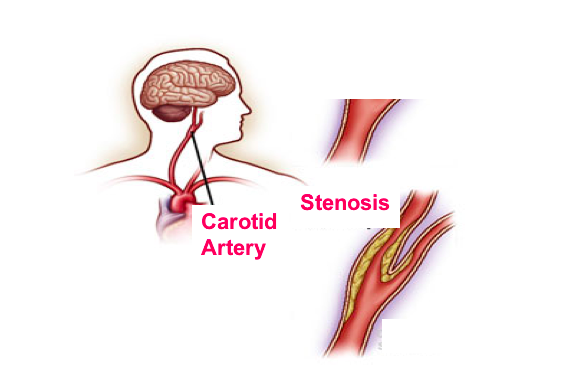
Carotid arteries are the main vessels located on left and right sides of your neck that deliver blood to your brain and head. If these arteries are narrowed or blocked by a fatty plaques there might be insufficient blood and oxygen delivery to brain tissues.
In cerebrovascular diseases, dizziness is almost the first symptom. In some cases, the first symptom in patients may be a stroke. In this case, medication, stent or surgical treatment, whichever is suitable, is chosen considering the severity of stenosis.
One important point to note is that hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis) is a systemic disease and it is likely to involve entire arterial system in the body.
Risk Factors
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High Blood Pressure ( Hypertension )
- Family History
- High Blood Lipids
Stroke
Stroke is the major complication of the carotid artery disease. It can leave a permanent damage and in some cases it can be fatal.
Treatment
First you have to change your lifestyle.
- Quit Smoking
- Control Blood pressure
- Control Diabetes and High Blood lipids
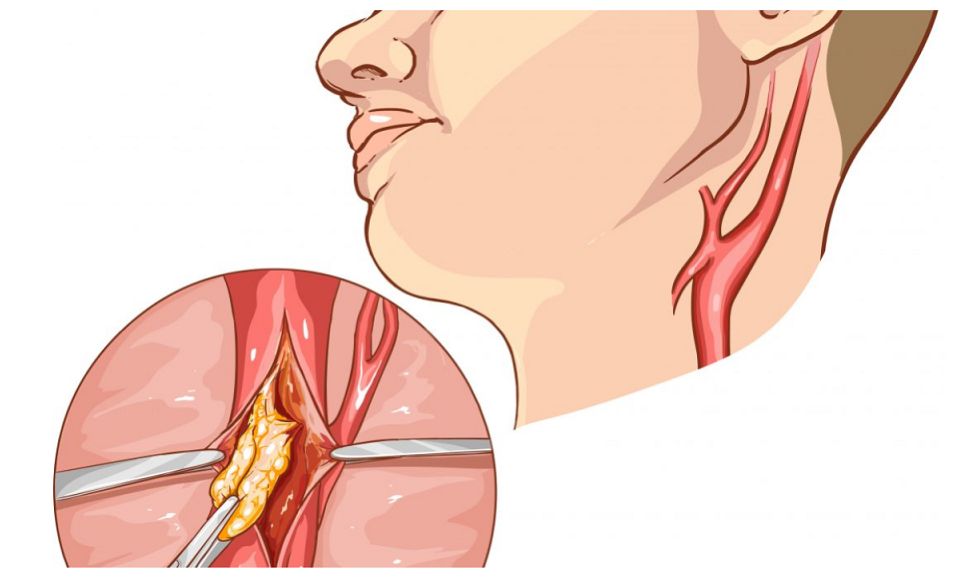
Carotid Endarterectomy or Carotid Artery Stenting
If you have a severe narrowing in your carotid arteries a surgical procedure called carotid endarterectomy or interventional procedure called carotid artery stenting may be an option for you. In carotid endarterectomy, a small incision is made along your neck under general or local anesthesia. Carotid artery is opened and a fatty plaque is removed . Then the artery is fixed. In Carotid artery stenting, a stent is placed to the narrowed segment through a femoral artery.
PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASES
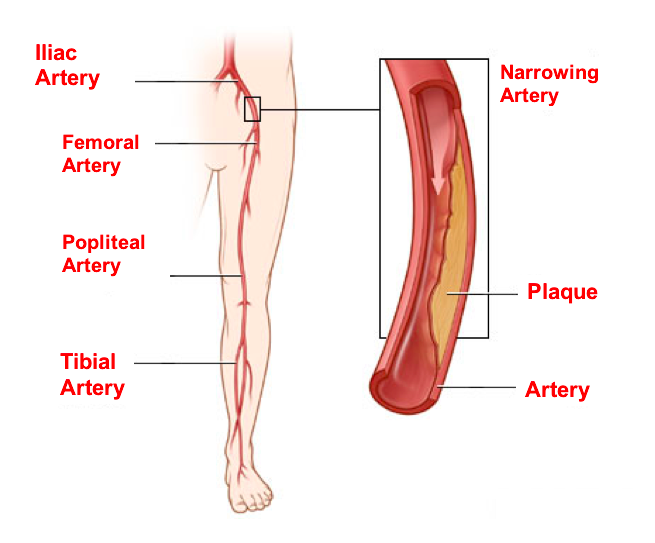
Peripheral means away from the heart. In this case it affects the arteries serving the legs, arms head and visseral organs. Most commonly it is a circulatory problem in which the narrowed arteries reduce the blood flow to your limbs. The major factor causing arterial blockage is the vessel stiffness (atherosclerosis).
Risk Factors for Peripheral Arterial Diseases
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Hypertension ( High Blood Pressure )
- Obesity
- High blood lipids ( cholesterol )
- Family history for atherosclerosis, heart disease or stroke
What are the symptoms of PAD ?
Pain (Claudication)
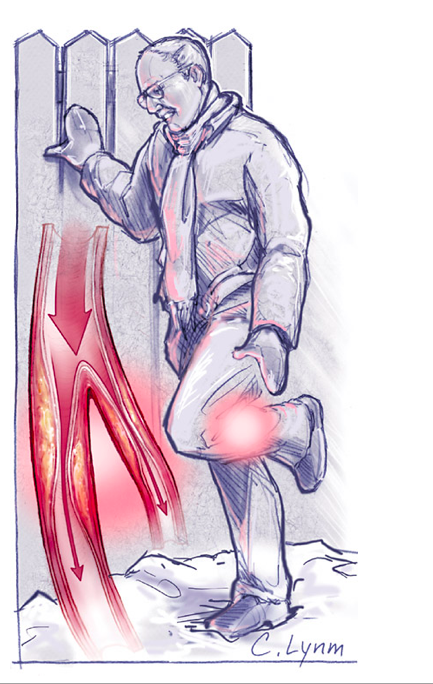
The most important symptom in peripheral artery diseases is the onset of pain on calves and thighs during walking (Claudication). In this case, there may be a blockage in the arteries coming from the abdomen going to both groins and/or in the vessels from coming from the groins going down to the knee and below-knee areas. Blockage means a decrease in the amount of blood supplied to the leg. This causes the blood flow to be sufficient during rest, but insufficient during mobility. In general, the pain disappears following a 1-2 minute rest.
Changes in legs and arms
- Reduced hair growth, cramps,
- Thin or pale skin,
- Weak Pulses
- Wounds or ulcers that wont heal
Erectile dysfunction in men
Does blockage disappear by itself ?
No, it does not. But, the amount of blood flow supplied to the leg increases as new minor vessels (capillaries) emerge nearby, in time (collateral circulation). At the same time, the leg muscles adapt themselves to the reduced blood flow. The pain complaint usually begins to remit within two-three months.
How do we notice it?
When we check our foot pulses, we will notice they have disappeared. A further investigation is performed via a Doppler ultrasonography. Angiography can also be performed, if required.
Is treatment necessary?
The onset of claudication is in fact a warning. And also, there might be some sort of blockage in the vessels supplying blood to our heart. You must see a doctor for a further examination. If the complaint is limited with the pain felt during walking only and is not increasing over time; then you can be monitored by checking the blood pressure, weight, diabetes and blood fats. If your walking distance decreases in a way to disturb your living quality, you still feel the pain when you take a rest and you suffer from wounds in your feet even though your risk factors are taken under control; then you may need a surgical treatment.
What are the treatment methods?
First, You have to reduce your risk factors
- Quit smoking if you are a smoker. A patient who continues smoking is unlikely to benefit from the treatment. In addition to that, the blood pressure should be checked regularly, blood fats should be kept under certain levels and your glucose level should be under control if you are a diabetic.
- Regular exercise: Walking longer than 30 minutes at least three times a week leads to a significant increase in walking distance within 3-6 months.
- Medication: It is known that some blood thinning drugs increase the walking distance. Your doctor will prescribe the most appropriate medicine for you.
Endovacular treatment or Bypass surgery: If a large section in your vessel is blocked, your complaints may increase in spite of the exercises and medication. If you get a colour change and wounds on your feet; you may need a interventional treatment or bypass surgery for the blocked section. Remember! Surgical intervention is the final option in this disease.
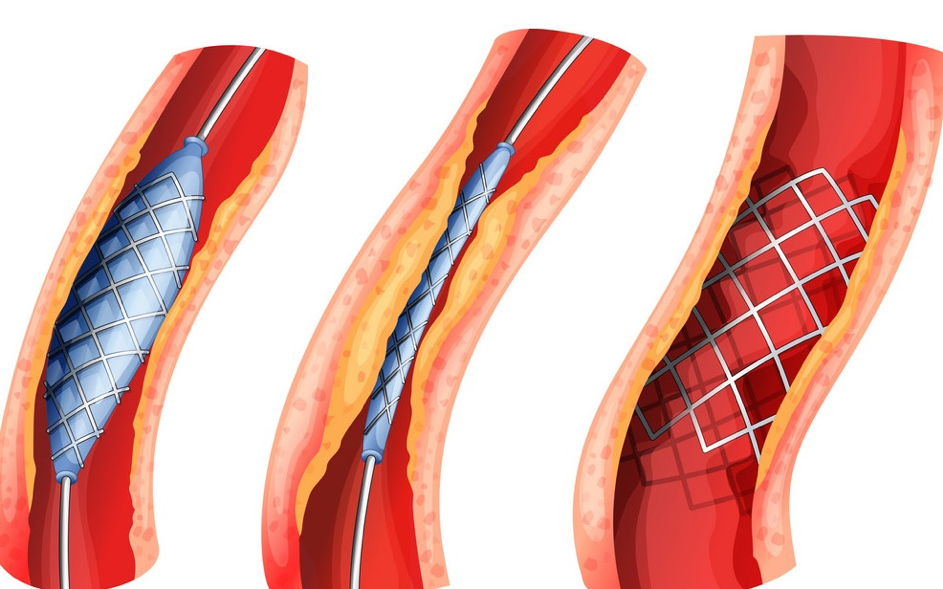
Advanced peripheral arterial disease can be treated with interventional methods such as angioplasty or stent placement.
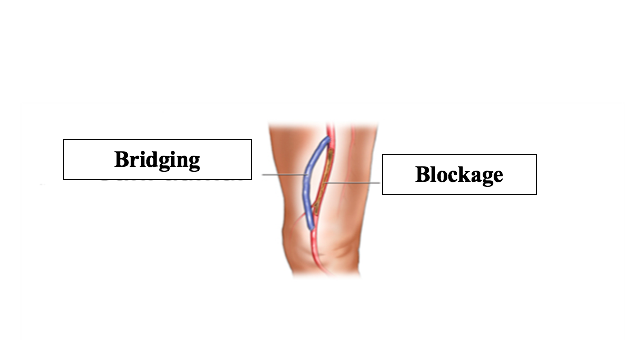
If the disease extensive and is not suitable for interventional methods, a synthetic graft or a blood vessel from another part of body is used to redirect blood flow around a occluded or narrowed artery.
VARICOSE VEIN
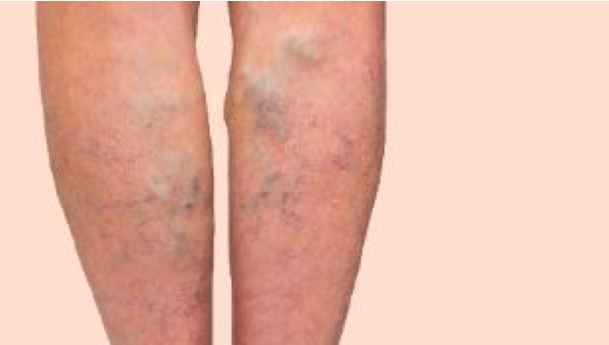
Varicose vein is a common disease widely seen in the community. It can be described as swollen bulging veins that protrude from the surface of the skin with blue or purpish color. In the first phase of the disease, capillary level enlargements are more prevalent while, in later stages, the enlargement occurs in the veins thicker in diameter. In the most advanced phase, open wounds called “ulcer” emerge particularly in the inner parts of the leg.
Pain, oedema and cramps are common symptoms in varicose patients. The definitive diagnosis is made by “Doppler ultrasonography”. Treatment is scheduled based on the findings of Doppler ultrasonography. In general sense, for the patients with severe aesthetic complaints, drug treatment (sclerotherapy) or laser applications are preferred for capillaries while interventional methods (Laser or Radiofrequency) or surgical methods are preferred in the case of enlargements in thicker veins.
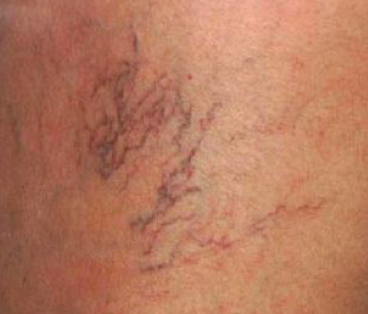
A patient with prominent enlargement of capillaries.
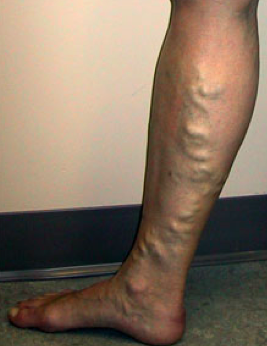
A typical varicose vein patient
What are the advantages of Laser or Radiofrequency Methods?
The symptoms of bruising and pain seen in classical varicose surgeries are much less common when laser or radiofrequency methods are applied. Patients can return to their daily routine in a much shorter time.
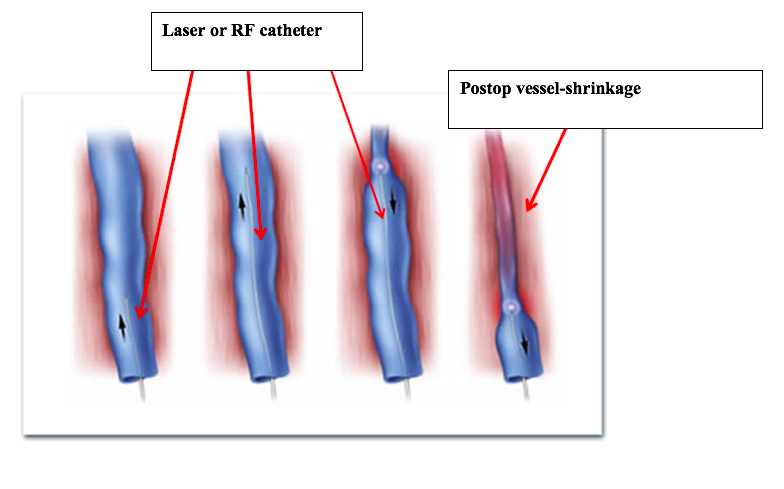
Once the laser or radiofrequency catheter is inserted into the vein, it is moved up to the groin region and retracted again in order to shrink the vessel.
